Jun 29,2025
Unlock Efficiency: How Automated Machining Transforms Manufacturing Processes
Automated machining is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, offering businesses opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality
1. Introduction to Automated Machining
Automated machining represents a profound shift in manufacturing processes, enabling businesses to enhance productivity while reducing operational costs. In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, companies are compelled to adapt to new technologies to maintain competitiveness. Automated machining systems integrate advanced robotics and computer numerical control (CNC) technologies, streamlining workflows and minimizing human error. This article delves into the transformative power of automated machining, examining its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
2. Understanding Automated Machining Systems
Automated machining encompasses various technologies designed to perform manufacturing tasks with minimal human intervention. These systems often utilize **CNC machines**, robotics, and other automated tools to produce components with precision. By programming these machines, manufacturers can achieve consistent quality and output, ensuring that products meet rigorous specifications.
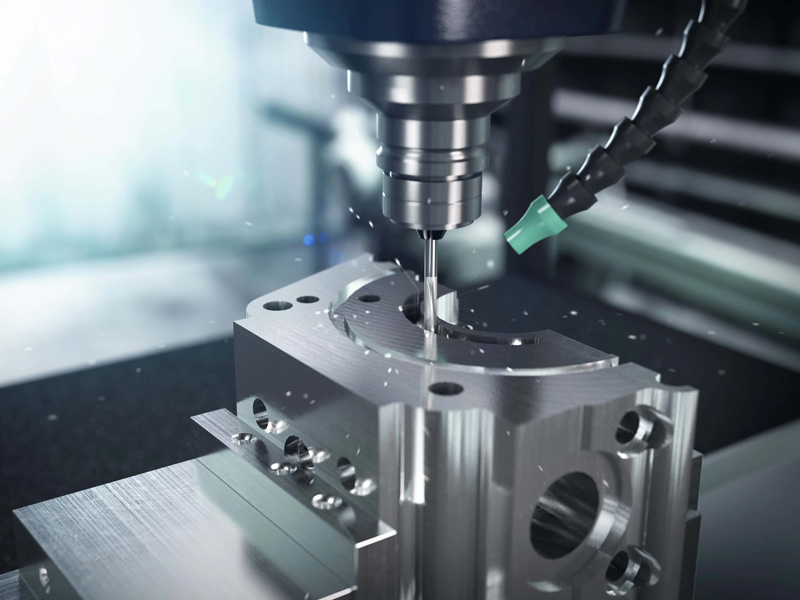

2.1 Components of Automated Machining
Key components of automated machining systems include:
- **CNC Machines**: These machines are programmed to cut, mill, and shape materials into desired forms with high precision.
- **Robotic Arms**: Employed for various tasks, robotic arms enhance efficiency by performing repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy.
- **Software Solutions**: Advanced software helps in designing, monitoring, and controlling manufacturing processes, enabling real-time adjustments and improvements.
3. Key Benefits of Automated Machining in Manufacturing
The adoption of automated machining systems offers numerous advantages that significantly improve manufacturing efficiency.
3.1 Enhanced Precision and Quality
Automated machining systems deliver **exceptional accuracy** in production, minimizing variations and ensuring that every piece meets the required specifications. The high repeatability of these systems results in fewer defects and a better overall product quality.
3.2 Increased Production Speed
With the capability to operate continuously without fatigue, automated machining can dramatically increase production rates. This allows manufacturers to meet higher demand without compromising quality, leading to greater profitability.
3.3 Cost Savings
Though initial investment in automated machining can be significant, the long-term savings are substantial. Businesses benefit from reduced labor costs, decreased material waste, and lower operational expenses. The return on investment (ROI) is often realized within a few years as production efficiency improves.
3.4 Flexibility and Scalability
Automated machining systems can be easily reprogrammed to manufacture different products. This flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to market changes and scale operations as needed without extensive retooling.
4. Technologies Driving Automated Machining
Several key technologies are at the forefront of automated machining, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher levels of efficiency and precision.
4.1 Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technologies facilitate real-time data collection and analysis, allowing manufacturers to monitor machine performance and optimize processes. This connectivity leads to predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
4.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI algorithms can analyze data from automated machining systems to identify patterns and suggest improvements. This intelligent approach to manufacturing helps companies make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and output.
4.3 Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, complement traditional machining processes. They enable the creation of complex geometries and reduce material waste, offering new possibilities for product design and production.
5. How to Implement Automated Machining in Your Factory
Implementing automated machining requires a strategic approach to ensure successful adoption and integration into existing processes.
5.1 Assessing Your Needs
Begin by evaluating your manufacturing requirements. Identify bottlenecks in your current processes and determine which tasks could benefit most from automation.
5.2 Selecting the Right Technology
Research and select the appropriate automated machining technologies that align with your manufacturing goals. Consider factors such as machine capabilities, ease of integration, and support from suppliers.
5.3 Training Employees
A successful transition to automated machining depends on having a skilled workforce. Provide training programs for employees to familiarize them with the new technologies and processes.
5.4 Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Once automated systems are in place, continuously monitor their performance. Use data analytics to identify areas for improvement and adapt processes as necessary.
6. Challenges of Automated Machining and Solutions
While automated machining presents numerous benefits, it also poses certain challenges that must be addressed.
6.1 High Initial Investment
The upfront costs of purchasing and implementing automated systems can be daunting. To mitigate this, consider a phased approach to automation, allowing for gradual investment while assessing ROI.
6.2 Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating new automated systems with legacy equipment can be complex. Work with experienced automation consultants to ensure seamless integration and minimize disruptions.
6.3 Skill Gaps in Workforce
The shift to automated machining may leave some employees feeling overwhelmed. Invest in ongoing training and support to help your workforce adapt to new technologies comfortably.
7. Case Studies: Success Stories in Automated Machining
Examining real-world examples of companies that successfully implemented automated machining can provide valuable insights.
7.1 Case Study: Precision Components Manufacturer
A precision components manufacturer adopted automated CNC machining to enhance production speed and accuracy. As a result, they increased their output by 40% while reducing material waste by 30%. This success led to a significant boost in their market position.
7.2 Case Study: Automotive Parts Producer
An automotive parts producer integrated robotic arms into their assembly line, drastically reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. The automated system allowed them to meet the growing demand for electric vehicles without compromising quality.
8. The Future of Automated Machining
The future of automated machining promises even greater advancements as technology continues to evolve. Innovations such as **machine learning**, **advanced robotics**, and **smart factories** will redefine manufacturing processes.
8.1 Emphasis on Sustainability
As industries move toward sustainability, automated machining will play a crucial role in reducing waste and energy consumption. Technologies that optimize resource use will become more prevalent.
8.2 Increased Customization
The rise of consumer demand for personalized products will drive further automation in machining. Manufacturers will adopt flexible systems that allow for small-batch production without sacrificing efficiency.
Automated machining is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, offering businesses opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. By understanding the technologies that drive automation and addressing the associated challenges, manufacturers can successfully navigate the evolving industrial environment. Embracing these advancements not only positions companies for immediate gains but also prepares them for a future where adaptability and innovation are key to sustained success. As industries continue to evolve, automated machining will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of this transformation, unlocking new levels of productivity and efficiency in manufacturing.
Previous: Understanding Mechanical Machining: A Comprehensive Guide
Next: The Essential Guide to Precision Parts in Manufacturing